
The data were obtained from epithelial sheets of the base of the oral cavity ( A,B, D–F) and palate ( C) immunoreacted against Vimentin. Quantitative analysis of total taste bud number ( A–C), total number of bud clusters ( D), and number of taste buds per cluster ( E,F) in chickens at selected stages (P0–8). Our protocol for labeling taste buds with molecular markers will factilitate future mechanistic studies on the development of chicken taste buds in association with their feeding behaviors. In addition to ovoid-shaped taste buds, big tube-shaped taste buds were observed in the chicken using 2-photon microscopy. Broiler-type, female-line males have more taste buds than other groups and continue to increase the number of taste buds over stages after hatch. In the peeled epithelial sheets, taste buds labeled with antibodies against Vimentin and α-Gustducin were easily identified and counted under a light microscope and many more taste buds, patterned in rosette-like clusters, were found than previously reported with SEM. Immediate tissue fixation following incubation with sub-epithelially injected proteases enabled us to peel off whole epithelial sheets, leaving the shape and integrity of the tissue intact. Here, we report a highly efficient method for labeling chicken taste buds in oral epithelial sheets using the molecular markers Vimentin and α-Gustducin. There is not an easy way to visualize all taste buds in chickens. It is here that taste signals are combined with different smell signals.In chickens, the sensory organs for taste are the taste buds in the oral cavity, of which there are ~240-360 in total number as estimated by scanning electron microscopy (SEM). The other fibers pass over these exchange points of conscious perception and leads directly to the parts of the brain that are connected with sensory perception and which are responsible for securing our survival.

At that point there is a split: Some fibers carry taste signals together with signals from other sensory perceptions like pain, temperature or touch through several exchange points to consciousness. All information is carried along the cranial nerves to part of the lower section of the brainstem (the medulla oblongata).

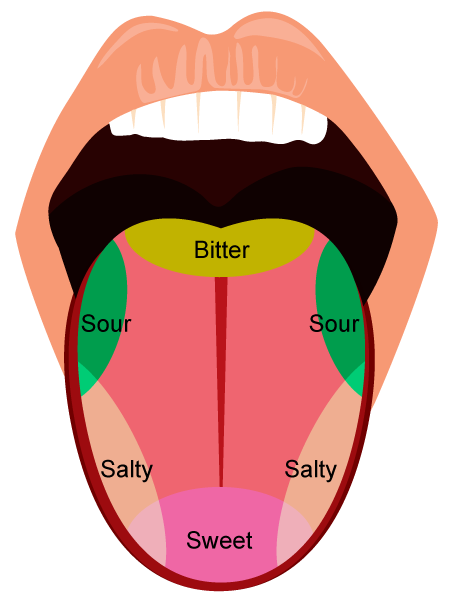
The final step in perceiving taste is transfer to the nervous system. Infants and young children also have sensory cells on their hard palate, in the middle of their tongue as well as in the mucous membranes of their lips and cheeks. But there are also cells that detect taste elsewhere inside the oral cavity: in the back of the throat, epiglottis, the nasal cavity, and even in the upper part of the esophagus. Most of the taste buds are on the tongue. The sensory cells in the taste buds are renewed once a week. Adults have between 2,000 and 4,000 taste buds in total. The taste buds are located in the walls and grooves of the papillae. This makes sure that the substances are detected and analyzed by as many sensory cells as possible before being swallowed. The chemical substances responsible for the taste are washed into this funnel-like hollow.

In the middle of the top side is a small indentation filled with fluid. These bumps, which are called taste papillae, contain many sensory cells with a special structure: together with other cells they make up a bud that looks a bit like an orange with its sections arranged around a center. The numerous wart-like bumps on the mucous membrane of the tongue are where the substance producing the taste is transformed into a nerve signal. These nerve cells then pass information for a particular perception of flavor on to the brain. This change causes the sensory cell to transmit messenger substances, which in turn activate further nerve cells.
It activates the cell by changing specific proteins in the wall of the sensory cell. It starts at the tongue: From substance to tasteīut what is taste actually? What happens in our body that enables us to perceive flavor? The chemical substance responsible for the taste is freed in the mouth and comes into contact with a nerve cell.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
